区块同步
博主的朋友写的
- 看到
core\blockchain.go的时候大量涉及该部分知识,故在此参考大佬博客加之自己的理解先行总结- 本文仅仅是简单总结了一下文件结构和重要函数功能,详细函数分析请参考downloader 同步
文件结构
downloader 模块的代码位于 eth/downloader 目录下。主要的功能代码分别是:
-
downloader.go:实现了区块同步逻辑 -
peer.go:对区块各个阶段的组装,下面的各个FetchXXX就是很依赖这个模块。 -
queue.go:对eth/peer.go的封装 -
statesync.go:同步state对象 -
注意:
-
downloader是一个下载器,从远程网络节点中获取 hashes 和 blocks。 -
fetcher则收集网络其他以太坊节点发过来的同步通知,进行验证,并做出相应的处理。 -
peers是经过验证可信任的通信节点的集合。 -
queuerepresents hashes that are either need fetching or are being fetched1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34// queue represents hashes that are either need fetching or are being fetched
type queue struct {
mode SyncMode // Synchronisation mode to decide on the block parts to schedule for fetching
// Headers are "special", they download in batches, supported by a skeleton chain
headerHead common.Hash // Hash of the last queued header to verify order
headerTaskPool map[uint64]*types.Header // Pending header retrieval tasks, mapping starting indexes to skeleton headers
headerTaskQueue *prque.Prque // Priority queue of the skeleton indexes to fetch the filling headers for
headerPeerMiss map[string]map[uint64]struct{} // Set of per-peer header batches known to be unavailable
headerPendPool map[string]*fetchRequest // Currently pending header retrieval operations
headerResults []*types.Header // Result cache accumulating the completed headers
headerProced int // Number of headers already processed from the results
headerOffset uint64 // Number of the first header in the result cache
headerContCh chan bool // Channel to notify when header download finishes
// All data retrievals below are based on an already assembles header chain
blockTaskPool map[common.Hash]*types.Header // Pending block (body) retrieval tasks, mapping hashes to headers
blockTaskQueue *prque.Prque // Priority queue of the headers to fetch the blocks (bodies) for
blockPendPool map[string]*fetchRequest // Currently pending block (body) retrieval operations
receiptTaskPool map[common.Hash]*types.Header // Pending receipt retrieval tasks, mapping hashes to headers
receiptTaskQueue *prque.Prque // Priority queue of the headers to fetch the receipts for
receiptPendPool map[string]*fetchRequest // Currently pending receipt retrieval operations
resultCache *resultStore // Downloaded but not yet delivered fetch results
resultSize common.StorageSize // Approximate size of a block (exponential moving average)
lock *sync.RWMutex
active *sync.Cond
closed bool
lastStatLog time.Time
}
-
同步模式
以太坊中区块同步包含以下三种模式:
-
full sync:
full模式会在数据库中保存所有区块数据,同步时从远程节点同步 header 和 body 数据,而 state 和 receipt 数据则是在本地计算出来的。在 full 模式下,downloader 会同步区块的 header 和 body 数据组成一个区块,然后通过 blockchain 模块的
BlockChain.InsertChain向数据库中插入区块。在BlockChain.InsertChain中,会逐个计算和验证每个块的state和recepit等数据,如果一切正常就将区块数据以及自己计算得到的state、recepit数据一起写入到数据库中。 -
fast sync:
fast模式下,recepit不再由本地计算,而是和区块数据一样,直接由downloader从其它节点中同步;state数据并不会全部计算和下载,而是选一个较新的区块(称之为pivot)的state进行下载,以这个区块为分界,之前的区块是没有state数据的,之后的区块会像full模式下一样在本地计算state。因此在fast模式下,同步的数据除了header和 body,还有receipt,以及pivot区块的state。因此
fast模式忽略了大部分state数据,并且使用网络直接同步receipt数据的方式替换了full模式下的本地计算,所以比较快。 -
light sync:从网络中同步所有区块头,不去同步区块体,也不去同步状态数据,仅在需要相应区块和状态数据时从网络上获取
简单总结:
SyncMode:
FullSync:从完整区块同步整个区块链历史FastSync:快速下载 Header,仅在链头处完全同步LightSync:仅下载 Header,然后终止
区块下载
区块下载流程示意图如下所示:
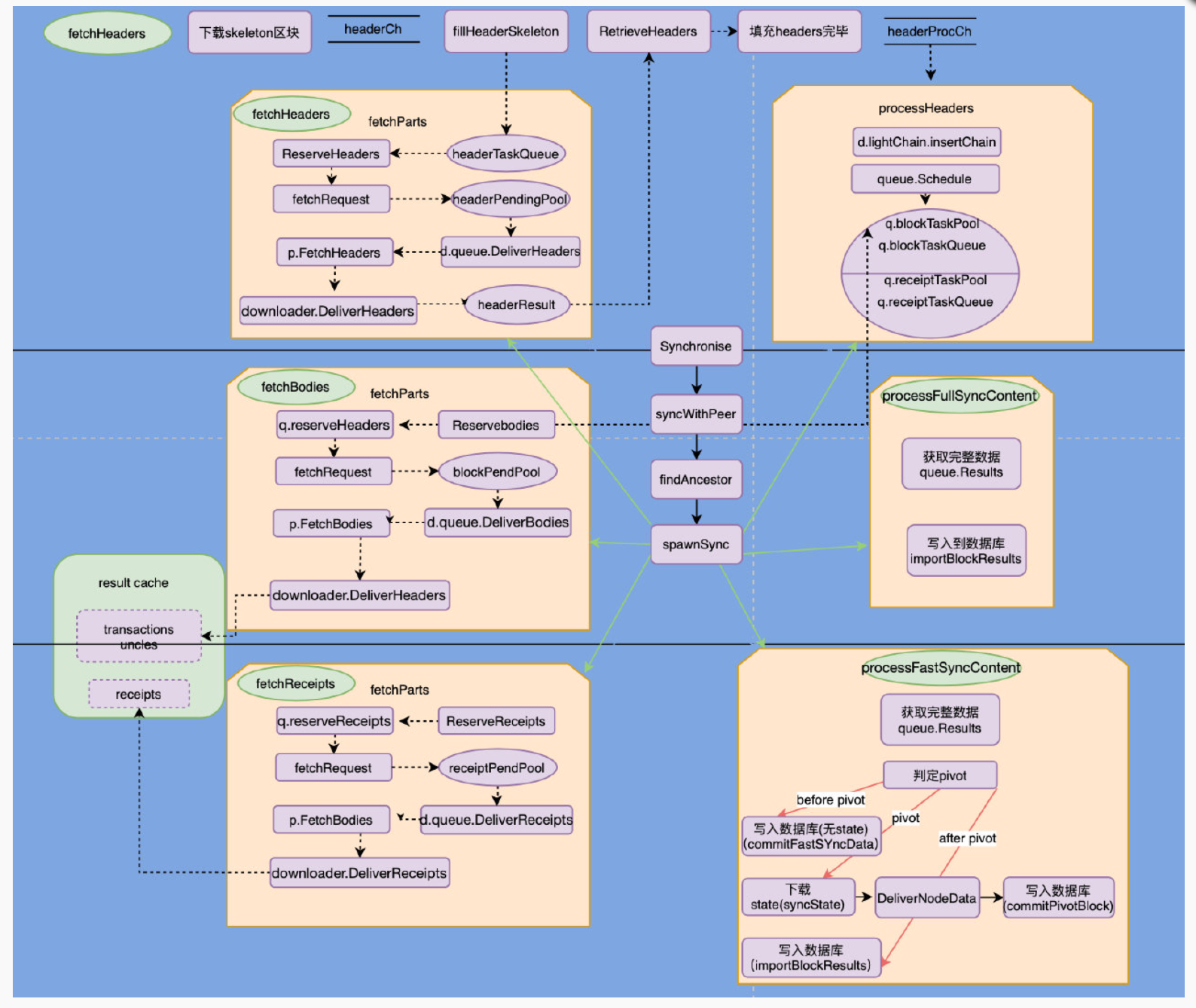
首先根据 Synchronise 开始区块同步,通过 findAncestor 找到指定节点的共同祖先,并在此高度进行同步,同时开启多个 goroutine 同步不同的数据:header、receipt、body,假如同步高度为 100 的区块,必须先 header 同步成功同步完成才可以进行 body 和 receipts 的同步,而每个部分的同步大致都是由 FetchParts 来完成的,里面包含了各个 Chan 的配合,也会涉及不少的回调函数
源码分析
数据结构
downloader 数据结构如下所示:
1 | type Downloader struct { |
构造方法
New 用于初始化一个 Downloader 对象,具体代码如下所示:
1 | // New creates a new downloader to fetch hashes and blocks from remote peers. |
同步下载
区块同步始于 Synchronise 函数,在这里会直接调用 synchronise 进行同步,如果同步过程中出现错误,则删除掉 Peer:
1 | // Synchronise tries to sync up our local block chain with a remote peer, both |
synchronise 函数实现代码如下:
1 | // synchronise will select the peer and use it for synchronising. If an empty string is given |
syncWithPeer 函数代码如下所示:
1 | // filedir:go-ethereum-1.10.2\eth\downloader\downloader.go L448 |
spawnSync 会给每个 fetcher 启动一个 goroutine, 然后阻塞的检查 fetcher 是否出错:
1 | // spawnSync runs d.process and all given fetcher functions to completion in |
同步 State
state 即世界状态,其保存着所有账户的余额等信息
1 | // filedir: go-ethereum-1.10.2\eth\downloader\statesync.go |
runStateSync 函数执行状态同步,直到它完成或请求切换到另一个根哈希:
1 | // runStateSync runs a state synchronisation until it completes or another root |
同步 Head
1 | // fetchHead retrieves the head header and prior pivot block (if available) from a remote peer. |
处理 Head
1 | // processHeaders takes batches of retrieved headers from an input channel and |
同步 Body
1 | // fetchBodies iteratively downloads the scheduled block bodies, taking any |
同步收据
1 | // fetchReceipts iteratively downloads the scheduled block receipts, taking any |
Content
1 | // processFullSyncContent takes fetch results from the queue and imports them into the chain. |
小问题
问题: light 节点与 full 节点是如何交互的?
解答: 首先,light 节点会维护多个与 full 节点的 p2p 连接。然后,当 light 节点需要与 full 节点交互时,会将需要发送的请求放到一个请求队列中。light 节点会启动一个 goroutine 不断从请求队列里获取请求,然后从 p2p 节点列表里选一个当前最好用的节点,将请求发出去。请求得到的结果会发到本地数据库和缓存里。
作者:Ashton
链接:https://www.jianshu.com/p/b31c208acaaa
来源:简书
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
转载于以太坊区块同步






